ARGUS Umweltbiotechnologie GmbH



© 2024 ARGUS Umweltbiotechnologie GmbH

Services
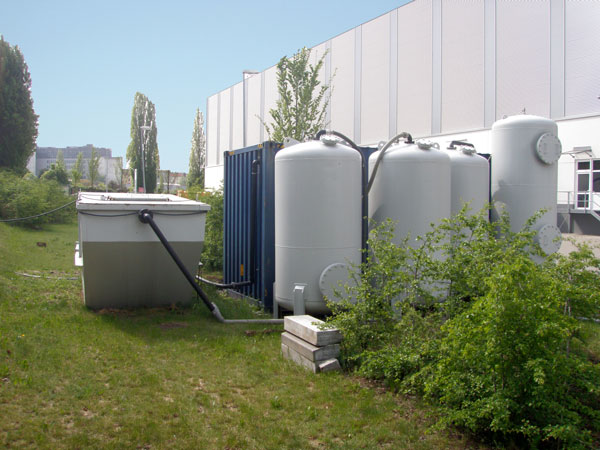
Groundwater treatment plant
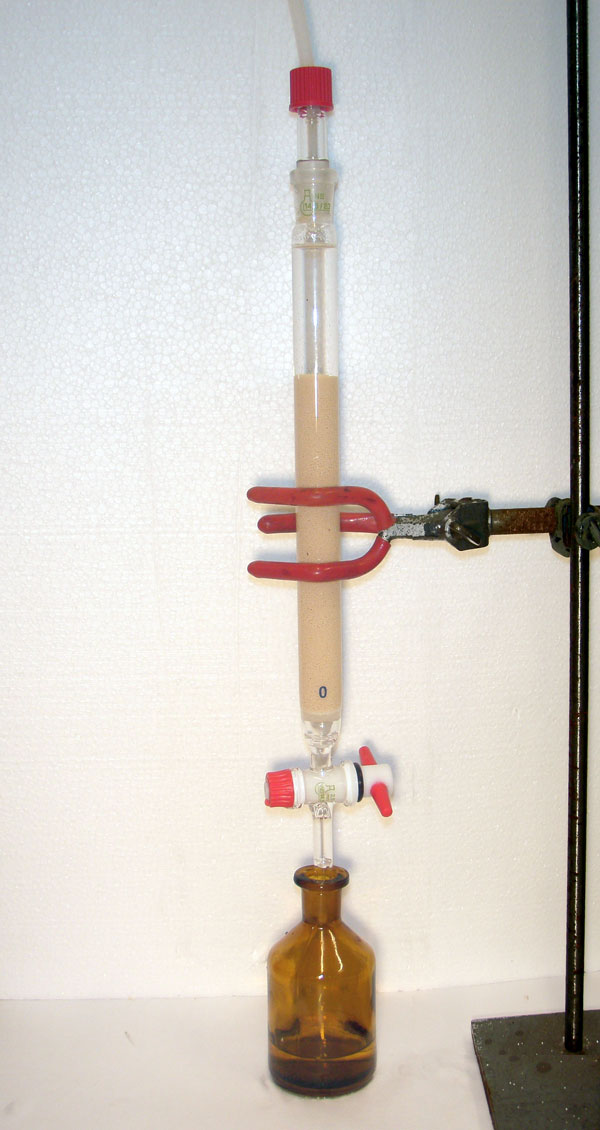
Anion Exchanger material
Laboratory test
Laboratory test
5
< BG
13
Phenol index
1.000
< BG
225
Mineral oil hydrocarbons on surfaces
10
< BG
127
BTEX
5
117
PAH (incl. Naphthalene)
50
< BG
1.740
Cyanides (Total)
Contaminant
Inflow
(Downstream)
in µg/l
(Downstream)
in µg/l
Outflow
in µg/l
in µg/l
permissible
limit
in µg/l
limit
in µg/l
Flow rate
4 m³/h
Anion Exchanger
2 x 1 m³ Fluidised bed process
Biological Stage
2 x 2 m³ Bio-Fixed Bed Reactor
Adsorption stage
2 x 2 m³ Activated Carbon
Remote Monitoring
Case Study Physical/Biological Groundwater Remediation
Massive groundwater contamination was discovered on a former gaswork site with elevated concentration of Cyanide (2.200µg/l), PAH (10.711µg/l, including Naphthalene 10.641µg/l), BTEX (10345 µg/l), Mineral-oil hydrocarbons (10.870µg/l) and subsidiary Phenols (not specified). The groundwater contamination source lies beneath a newly built storage hall and is therefore not directly accessible. ARGUS currently operates groundwater containment downstream from the contamination source.
Groundwater is collected along the entire width of the source zone in the downstream area using 4 groundwater extraction wells and is then directed to a central groundwater treatment plant. The groundwater treatment installation consists of a combination of physical and biological remediation methods.
Cyanide is initially removed from the groundwater using a 2-Stage Anion-Exchanger device. Groundwater is then subsequently liberated in a biological stage of the process as far as possible from the organic contaminants. A downstream activated-carbon filter ensures that pre-determined discharge limits are complied with. Remediated groundwater is then discharged into a rainwater drainage system.
Groundwater is collected along the entire width of the source zone in the downstream area using 4 groundwater extraction wells and is then directed to a central groundwater treatment plant. The groundwater treatment installation consists of a combination of physical and biological remediation methods.
Cyanide is initially removed from the groundwater using a 2-Stage Anion-Exchanger device. Groundwater is then subsequently liberated in a biological stage of the process as far as possible from the organic contaminants. A downstream activated-carbon filter ensures that pre-determined discharge limits are complied with. Remediated groundwater is then discharged into a rainwater drainage system.
Treatment Plant Specifications:
Contaminant Concentrations:
The degree of remediation in the Anion Exchange stage is 99.9%, in the biological stage 95% of the contaminants are extracted.
Pre-determined discharge limits set by the regulatory authorities were always met based on the total degree of remediation that was attained (99.9%).
Potential adverse effects on biodegradation from cyanide were avoided through the incorporation of the Anion Exchanger. Replacement of activated-carbon has still not been necessary due to the high degree of biodegradation.
The increasing concentrations of contaminants in inflow water into the treatment plant show that the contamination can be mobilised and caught through the downstream containment measures.
Pre-determined discharge limits set by the regulatory authorities were always met based on the total degree of remediation that was attained (99.9%).
Potential adverse effects on biodegradation from cyanide were avoided through the incorporation of the Anion Exchanger. Replacement of activated-carbon has still not been necessary due to the high degree of biodegradation.
The increasing concentrations of contaminants in inflow water into the treatment plant show that the contamination can be mobilised and caught through the downstream containment measures.